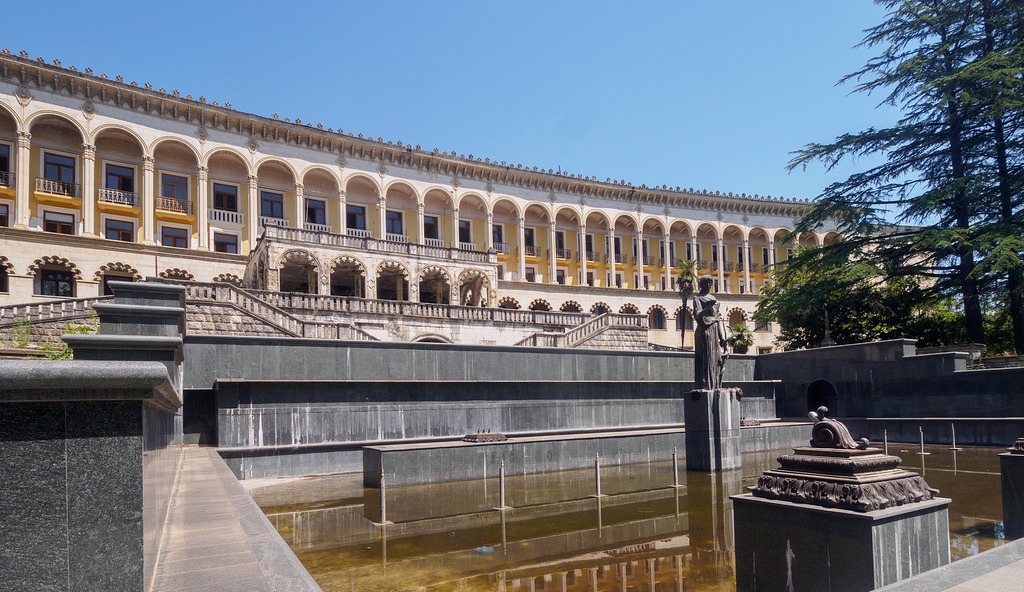
Mineral water Tskaltubo
The origin of Tshaltubo mineral water in geological terms is considered the oldest (100-150-year-old) in the formation of which involves modern hydrochemical processes. However, believe that the formation of Tshaltubo water is due to the vast resources of underground static water to go the earth's surface balneologic zone due to the hydrostatic pressure of karst waters. According to the hypothesis of a mixed-rich chlorine water rises from the Middle Jurassic deposits, mixed with sulfate water of the upper crust, and then in the Lower Cretaceous limestones hydrocarbonate desalt water. Restocking tshaltubo mineral water is mainly due to precipitation falling on the slopes Samguralskogo ridge. Enrichment of radon Tshaltubo mineral water occurs in the sands of alluvial deposits. Tshaltubo mineral springs have always attracted the attention of the sharply differing properties from other medical treatment. Due to the absence of toxic elements of water has a gentle action, and the procedures are easily tolerated.In tshaltubo mineral springs were found biologically active trace elements: iodine, bromine, manganese, lithium, boron, zinc, strontium, copper, which, despite the fact that are contained in small amounts, plays an important role in the life of the organism. Significant role in tshaltubskih sources are gases: nitrogen, radon, helium, argon.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF MINERAL WATER TSKALTUBO
|
Chemical elements |
Grammes |
Equivalent |
Equivalent % |
|
Cations |
|||
|
Na+K |
0,0534 |
2,32 |
20,33 |
|
Mg |
0,0341 |
2,84 |
24,89 |
|
Ca |
0,1250 |
6,25 |
54,78 |
|
Fe |
0,0011 |
--- |
--- |
|
Sum |
0,2136 |
11,41 |
100,00 |
|
Anions |
|||
|
Cl |
0,1012 |
2,85 |
24,98 |
|
SO4 |
0,2237 |
4,66 |
40,84 |
|
HCO3 |
0,2079 |
3,90 |
34,18 |
|
Sum |
0,5628 |
11,41 |
100,00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SiO |
0,242 |
--- |
--- |
|
Al2O3F2O3 |
0,0029 |
--- |
--- |
|
Total mineralization |
0,8 |
--- |
--- |
|
CO2 |
0,088 |
--- |
--- |
|
The dry residue 110О |
0,764 |
--- |
--- |