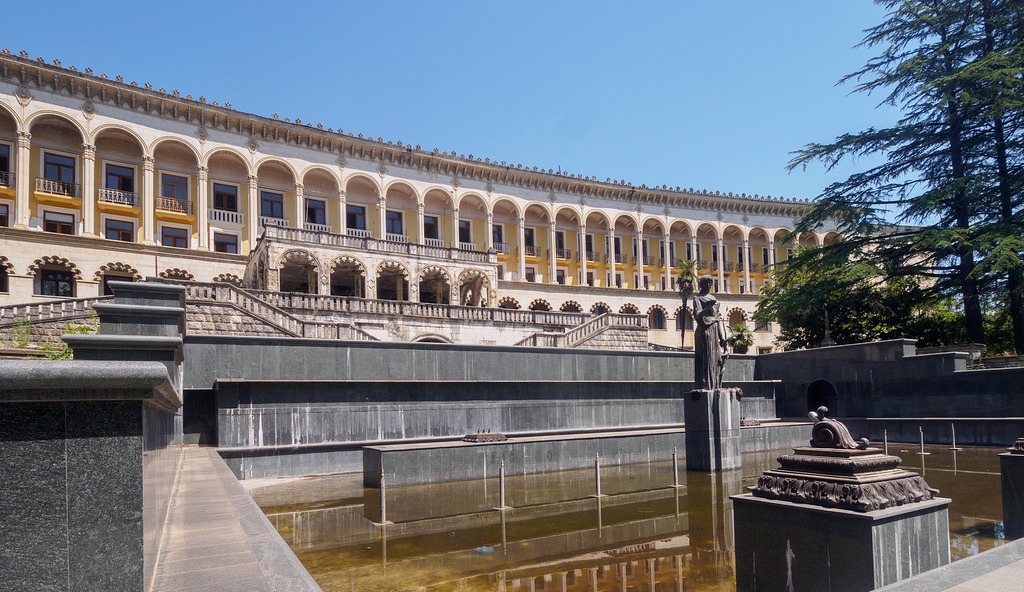
Indications and Contraindications for Radon therapy
(Indications and contraindications for the resort of Tskaltubo)
Specific contraindications for radon therapy are:
1. Radiation sickness;
2. Hypothyroidism;
3. Hypoestrogenism;
4. Individual intolerance to procedures.
The remaining contraindications are common for balneotherapy:
1. All diseases in the acute phase, chronic diseases in acute phase and complicated by acute purulent processes;
2. Acute infectious diseases before the end of isolation period;
3. All venereal diseases in the acute and contagious form;
4. Mental illnesses; all forms of drug addiction, alcoholism. Epilepsy;
5. All blood diseases in the acute stage and during exacerbation;
6. Cachexia of any origin;
7. Malignant neoplasms;
8. Repetitive or heavy bleeding;
9. Pregnancy in all periods – for the spa resorts and mud, but as for the climatic health resorts, starting from the 26 -th week;
In addition, in all stages of pregnancy one should not treat a pregnant female at health resorts and sanatoriums for:
a) balneological mud treatment of gynecological diseases;
b) for the treatment of extragenital diseases by radon baths;
c) Inhabitants of the plain areas to the mountain resorts located at an altitude of 1000 m above sea level
10. All forms of tuberculosis in an active stage - for all resorts and the sanatoria of nontuberculosis profile.
INDICATIONS FOR RADON THERAPY
(Indications for the resort of Tskaltubo)
Indications the Diseases of the Circulatory System
1. Rheumatoid endomyocarditis, primary or recurrent endomiocarditis of a prolonged or latent progress, with the minimal 1st degree of activeness of the procees on the background of the valvular heart damage and without thereof in circulatory failure, no more than of the 1-st stage, after 6-8 months since the end of the acute symptoms, without signs of the process to be in the active stage.
2. Diseases of the mitral valve: a) heart disease, mitral insufficiency, with no signs of activity of the process, with the state of compensation when circulatory failure is not more than in the 1st stage, and b) combined mitral heart disease with a predominance of mitral valve insufficiency, with no signs of activeness of the process – in times of evidence of a state of compensation or circulatory failure, at no more than the 1st stage, and c) combined mitral heart disease with prevalence of stenosis of the left antrioventricular canal defects, with no signs of activity at the state of compensation or circulatory failure, at no more than the 1-st stage d) period of 6-8 months after the mitral commissurotomy; after the surgery, in case of absence of activity of rheumatic processes in compensation or circulatory failure; a stage without cardiac arrhythmias.
3. Myocarditis, the condition after suffering an infectious-allergic myocarditis, in case of the acute and subacute occasion, after 6-8 months after the acute symptoms disappear when blood flow or lack of compensation is not higher than of the 1-st phase.
4. Angina: a) rare angina (1-2 times per week) at considerable physical effort (I and II functional classes), with circulatory failure not more than of the 1-st stage, without cardiac rhythm and conduction during long-term stable disease course.
5. Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis without angina without cardiac rhythm and the conduction in the circulatory failure, not exceeding 1 tbsp.
6. Hypertensive heart disease: 1) stage 1 hypertension and benign course, without frequent hypertensive crises, no prognostically adverse cardiac rhythm and conduction, and circulatory failure, no more than of the 1-st phase, 2) hypertension stage II A, benign course, without frequent hypertensive crises without adverse prognostic of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction (exceptions - sinus arrhythmia, single extrasystoles) in circulatory failure, no more than of the 1-st stage.
7. Hypotension. Hypotonic disease (essential hypotension).
8. Neuroses, neurosis with a predominant dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, with moderately severe common nerve syndromes.
9. Cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy due to surge of the heart muscle, as well as the of exchange, endocrine, toxic or infectious origin, with circulatory failure, no more than of the 1-st stage.
Peripheral vascular disease
1. Atherosclerosis of arteries: atherosclerosis of vessels of the extremities (without ulcers, gangrene) after surgery of the peripheral vessels (6-8 weeks after surgery).
2. Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's b-Hb), obliterating endarteritis with blood circulation disorders of lower limbs, of I and II degree in the period of stable remission.
3. Varicose veins of lower extremities: chronic venous insufficiency on the basis of varicose veins.
4. Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis of the lower limbs: Residual symptoms after phlebitis, thrombophlebitis of lower extremities: a) after acute or subacute effects, no earlier than 4 months after deep vein thrombophlebitis (post-trombophlebitic syndrome) and 2 months after the surface, and b) with venous insufficiency after thrombophlebitis, which is accompanied by trophic skin changes tibia (infiltrates, varicose ulcers).
General notes:
1. When recommending spa therapy for patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, one should take into account their reaction to the change of weather, and refrain from sending patients with meteotropic reactions in periods of sharp fluctuations in weather, especially during the cold period, as well as to resorts with contrasting climatic and geographical conditions. The patients with long-term stable diseases should be directed to the spa treatment.
2. In times of recommending the sanatorium and health resort treatment for the patients with cardiovascular disease, one should take into account the presence of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction, the nature of the disease. It is allowed to direct to the sanatorium and health resort treatment the patients with endocarditis, valvular disease, coronary heart disease, hypertension with occasional beats (up to 5 in 1 min.), Sinus arrhythmia, atrioventricular block of 1 degree and complete blockade of the right and left legs of bundle branch block.
Contraindications
1. Rheumatoid endiomiocarditis in the active phase (II, III degree of activity).
2. Myocarditis of Abramov-Fiedler type and close to it by severity.
3. Atherosclerosis of the lower limbs, with the presence of ulcers and gangrene.
4. Thromboangiitis obliterans (endarteritis) with a tendency to generalization in the presence of fresh ulcerations and gangrene.
5. Thromboembolic disease.
6. Thrombophlebitis within 1-2 years after the elimination of the septic process.
DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Statement
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system
1. Trigeminal neuralgia with rare attacks.
2. Neuritis and neuropathy of the facial nerve (in 2 months and later after the onset).
3. Defeat of the lumbosacral plexus lesions in the cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral spines of an inflammatory nature. The defeat of the brachial plexus (2 months or more after injury).
4. The defeat of the median nerve, ulnar and radial nerves; tunnel syndrome.
5. The defeat of the sciatic, femoral, peroneal, tibial nerves; tunnel syndrome.
6. Polyneuropathy during intoxication, poisoning, diabetes, and lack of vitamin B complex, and allergies.
7. Diseases of the intervertebral disc: cervical-cranial syndrome (posterior cervical sympathetic syndrome) caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
8. Degeneration of intervertebral discs in the cervical spine: neurodystrophic, radicular syndromes, shoulder-shoulder periarthrosis.
9. Degeneration of intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine: lumbodynia, sciatica and muscular-tonic, vegetative-vascular.
10. Displacement of intervertebral disc without myelopathy: discogenic sciatica.
11. Postlaminectomy syndrome; a state after a rupture disc herniation, lumbodynia, sciatica; subsequent to surgery and laminectomy after 3 months.
12. Injuries to the nerve root and plexus, spinal nerves, peripheral nerves of shoulder girdle and upper extremities, pelvic girdle and lower limbs.
13. Diseases of the autonomic nervous system: autonomic polyneuropathy solyarity, simpatoganglionity after the acute period.
Central nervous system diseases
14. Arachnoiditis, meningitis of the brain: cerebral arachnoiditis in remission after 3-6 months since the onset.
15. Encephalitis, myelitis and encephalomyelitis: residual effects after suffering a tick-borne,vaccination, rheumatoid and other forms of encephalitis after the acute period, not earlier than 4 months after the disease.
16. Long-term effects of acute poliomyelitis in the restorative and residual periods, as well as after the orthopedic surgery (3-6 months after the disease).
17. Benign neoplasms, the consequences of total removal of benign extramedullary tumors of the spinal cord: neurinomas, arahnoidendoteliom not before 4 months after surgery.
18. Spine fracture with spinal cord injury: hematorrhachis, cauda equina injury, with concussion of the spinal cord, with slight tetra-and paraparesis and others without limitation and self-movement and functional disorders of pelvic organs. 4 months after injury.
19. Syphilis of the central nervous system: amyelotrophy without pronounced ataxia, and cachexia.
20. Long-term consequences of intracranial injury. Brain injury: effects of the close (4 months) and open (5-6 months) of brain injury.
Cerebrovascular disease
21. Cerebral atherosclerosis: a) without circulatory disturbances, and b) in combination with hypertension of the I B and II and Stage, hypertensive encephalopathy without serious psychopathological disorders.
22. Transient ischemic attack within 3-4 months.
23. Vascular myelopathy 4 months after the acute period.
Functional and other diseases nervous system
24. Neurotic disorders: a) neurosis - hyper and hyposthenic forms, irritable weakness, neurosis, asthenic and neurosis-like states, and b) vegetative-vascular dysfunction due to infection, intoxication, trauma, endocrine disorders.
25. Raynaud's disease stage I-III and Raynaud's syndrome ganglion, vibration and other origin.
26. Neuromuscular disease: progressive muscular dystrophy: juvenile form of Erb-Roth, shoulder and facial juvenile form of Landuzzi-dejerine and other myopathies. Spinal amyotrophy Kugelberg-Welander. Neural amyotrophy of Charcot-Marie.
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
Arthritis and polyarthritis tubercular origin
1.The side effects of the traumas of rheumatic fever: no earlier than 8-10 months after the acute and subacute effects on the heart and no more than I degree symptoms of heart failure.
2.Rheumatoid arthritis: rheumatoid arthritis, mainly articular and clinically-combined forms in an inactive phase with the minimum and average activity of the process, in case of possibility of self-service of the patient.
3.Infectious polyarthritis of specific etiology: brucellosis, gonorrheal, post- typhoid metagrippal and others with an active process, not more than II degree.
Note. In chronic polyarthritis of brucellosis etiology spa treatment is indicated in cases where there is no febrile manifestations of brucellosis during the last 3 months.
4. Osteoarthritis, osteoarthrosis: deforming Osteoartrosis, dystrophic with secondary synovitis or without it.
5. Arthritis of traumatic origin.
6. Spondylosis, spondylarthrosis without sharp limits the mobility of the spine.
7. Osteochondrosis with secondary neurological disorders, and without that, in case of the independent movement of the patient.
8. Ankylosing spondylitis (Marie-Strumpell disease), arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis of spine.
9. Chronic infectious spondylitis (non-tuberculosis).
10. Intervertebral osteochondritis and osteomyelitis of the vertebral body.
11. Traumatic chronic spondylopathy.
12. The consequences of breaking a bone torso and extremities with delayed consolidation or painful bone spur.
13. Chronic synovitis and bursitis, tendovaginitah.
14. Myositis, neyromiozit.
15. Fibrositis, myalgia of infectious, toxic, occupational origin.
16. Epicondylitis, styloiditis as a result of voltage and changes the tone of autonomic nervous system.
17. Joint contractures and Dupuytren's contracture.
18. Chronic osteomyelitis: a) chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis (except tuberculosis), fistular (with recurrent course) do not require surgery or after it, and b) chronic osteomyelitis gunshot c) osteomyelitis after bone fractures without sequestration.
19. Traumatic amputation of the hand and fingers (3-4 months after surgery).
20. The consequences of burns: postburns contracture, including after the reconstructive surgery.
21. Chronic skin ulcer due to prolonged non-healing wounds.
16. Epicondylitis, styloiditis as a result of overexhaustion and changes the tonus of autonomic nervous system.
17. Joint contractures and Dupuytren's contracture
18. Chronic osteomyelitis: a) chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis (except tuberculosis), fistular (with recurrent course) do not require surgery or after it, and b) chronic osteomyelitis gunshot c) osteomyelitis after the bone fractures without sequestration.
19. Traumatic amputation of the hand and fingers (3-4 months after surgery).
20. The consequences of burns: postburns contracture, including after reconstructive surgery.
DISEASES OF FEMALE GENITALIA
1. Chronic salpingitis, oophoritis in the remission 2 months after the last exacerbation.
2. Chronic parameters in remission, 4-6 weeks after the acute process.
Note. In women older than 40 years the question of sanatorium treatment for this disease requires the advice of the oncologist.
3. Pelvic peritoneal adhesions.
4. Endomiometrit, subway.
5. Abnormal position of the uterus – (retroversion): retroflection (retrodeviation).
6. Infantilism (genital). Hypoplasia of the uterus.
7. Ovarian dysfunction.
8. Disorder of menstrual function. Secondary amenorrhea.
9. Scanty or infrequent menstruation.
10. Frequent and too profuse menstruation (polimenoreya, hypermenorrhea).
11. Irregular menstruation.
12. Symptoms of menopause.
13. State associated with artificially induced or premature menopause.
14. Infertility Female: 1) obstruction of the fallopian tubes, and 2) functional tubal infertility.
15. Complications after surgery: infiltration after operations on the uterus, tubes, ovaries with no signs of increasing.
Contraindications
1. Malignant tumors and a suspicion of their presence.
2. Postabortion period (before menarche).
3. Heat treatment-mud-and balneotherapy is contraindicated in:
a) erosion bleeding of the uterus;
b) polyps of the cervix;
c) diseases involving uterine bleeding;
d) cystoma and ovarian cysts;
d) uterine myoma, endometriosis and mastopathy;
e) The vesico-intestinal-vaginal fistula;
g) precancerous diseases of female genital mutilation, as well as the condition after surgery for malignant tumors.
DISRUPTION OF METABOLISM AND ENDOCRINE DISEASES
1. Obesity: the primary, alimentary and constitutive I-III degree, without the effects of circulatory decompensation.
2. Diabetes: latent, mild to moderate.
3. Gout.
4. Thyrotoxicosis, primary and secondary genesis mild.
Contraindications
1. Primary neuroendocrine (hypothalamic-pituitary), obesity, secondary cerebral, endocrine obesity of organic origin, and any forms of obesity in the IV degree of circulatory failure, and Article II above.
2. Diabetes mellitus, severe depletion, expressed ketoacidosis.
3. Severe thyrotoxicosis.
SKIN DISEASES
1. Psoriasis.
2. Neurodermatitis.
3. Scrapie.
4. Urticaria.
5. Planus.
6. Eczema.
7. Scleroderma: a) inactive stage, and b) with a lesion of the musculoskeletal system.
8. Hereditary keratosis, ichthyosis, keratoderma, hair lichen.
9. Acne.
10. Disorders of hair: baldness, seborrheic alopecia.
General remarks. In diseases of the skin worsening in the spring, patients should be directed to health-spa treatment in autumn and winter months, and in case of worsening in autumn and winter seasons of the year, in spring and summer.
Contraindications
1. All diseases of the skin in acute and subacute stages.
2. Cystic dermatosis.
3. Fungal infections of the scalp, smooth skin and nails.
4. Parasitic skin disease - scabies, etc.
5. Pustular skin diseases.
6. Reticulosis skin haemodermia
7. Lupus erythematosus, photodermatosis, late cutaneous porphyria, xeroderma pigmentosum.
UROLOGICAL DISEASES
1. Prostatitis, chronic non-tuberculosis vesicle stage remission, limited infiltration, without the structure of the urethra.